Evidence-based medicine is the driver for patient care at Inova. When spine surgery is required the surgeon will review procedure options that may be available. One of them might be minimally invasive spine surgery.
Compared to open spine surgery, minimally invasive spine surgery, sometimes referred to as MIS or MISS, accesses the spine through smaller incisions. These can be from 2-4 inches long compared to longer incisions in open approach spine surgery. Through the smaller incisions the surgeon is still able to move muscle tissue and expose the affected spine region.
The overall benefit to performing surgery with smaller incisions is for minimally invasive surgical approaches to be faster, safer and require less recovery time. Comparing this to open surgical approaches, there is reduced trauma to the muscles and soft tissues.
Some potential benefits to minimally invasive spine surgery include:
- Small incisions result in less scarring
- Reduction in soft tissue damage
- Less injury to the muscles
- Less post-operative pain
- Reduced blood loss
- Faster recovery
A note to understand: not all spine surgeries can be done with minimally invasive spine surgery techniques.
New techniques for minimally invasive spine surgery continue to evolve. Example conditions treated using minimally invasive surgical techniques include:
- Degenerative disc disease
- Herniated disc
- Lumbar spinal stenosis
- Spinal deformities such as scoliosis
- Spinal infections
- Spinal instability including spondylolisthesis
- Vertebral compression fractures
- Spinal tumors
Inova has the latest technologies for minimally invasive spine surgery with augmented reality and minimally invasive spine surgery with robotic instrumentation.
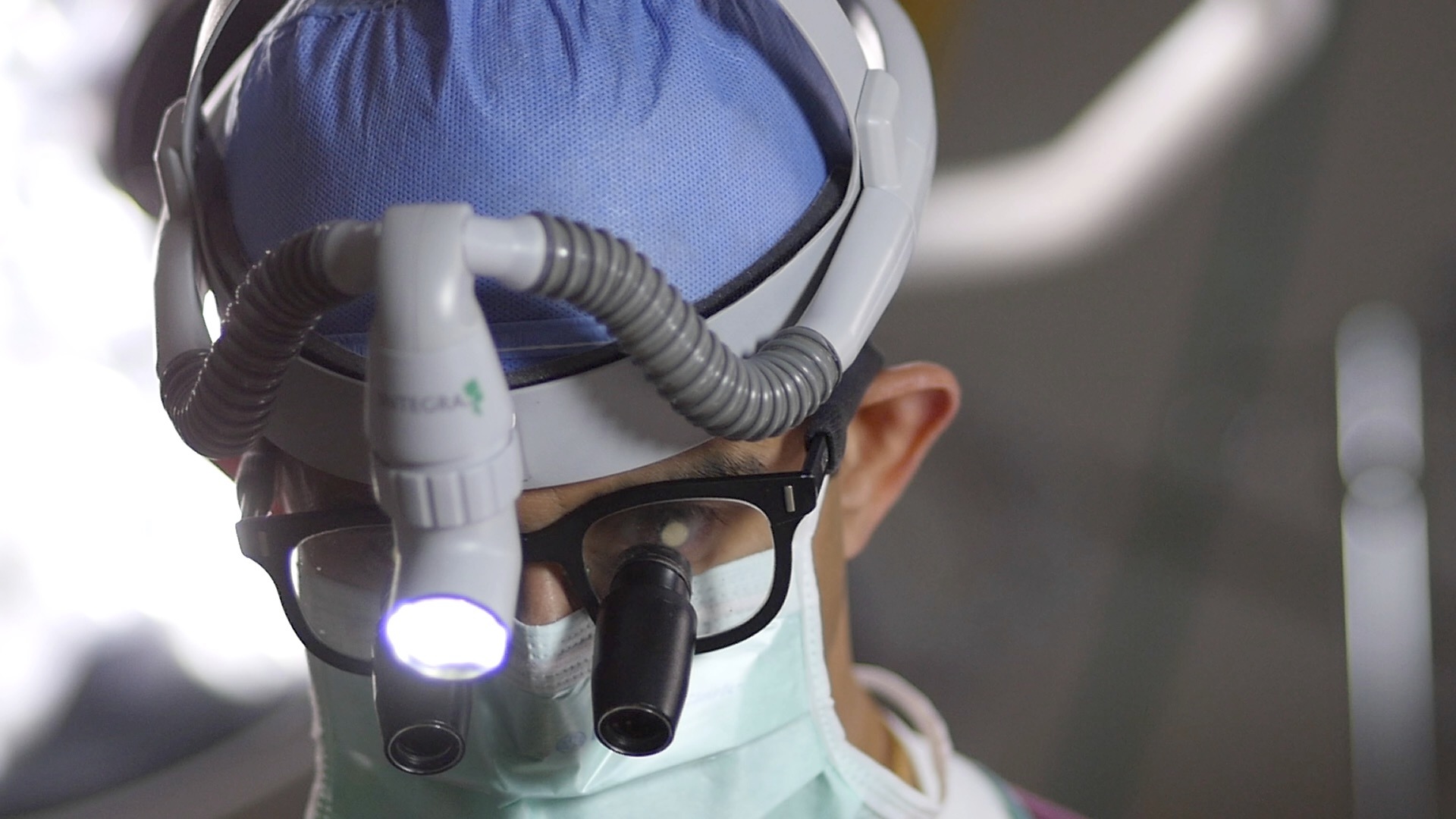
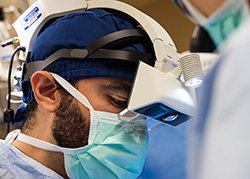 Augmented Reality (AR) guidance for spine surgery provides spine surgeons the ability to visualize the three-dimensional spine anatomy of a patient during surgery. This can be compared to working with "X-ray vision" glasses.
Augmented Reality (AR) guidance for spine surgery provides spine surgeons the ability to visualize the three-dimensional spine anatomy of a patient during surgery. This can be compared to working with "X-ray vision" glasses.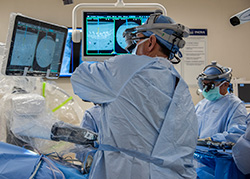 Robotic-assisted spine surgery is an advancement in spine surgery. It enables surgeons to plan their surgery even before their first patient cut. Once spine surgery begins, the robot provides screw placement with better accuracy due to the guidance system in the robot. Since the surgery was pre-programmed with prior imaging both the patient and operating room staff are subjected to less perioperative X-ray radiation. This minimally invasive surgery technique is more beneficial for the patient with a smaller incision, less pain, and other benefits noted under “
Robotic-assisted spine surgery is an advancement in spine surgery. It enables surgeons to plan their surgery even before their first patient cut. Once spine surgery begins, the robot provides screw placement with better accuracy due to the guidance system in the robot. Since the surgery was pre-programmed with prior imaging both the patient and operating room staff are subjected to less perioperative X-ray radiation. This minimally invasive surgery technique is more beneficial for the patient with a smaller incision, less pain, and other benefits noted under “